How to run cardano-node
Overview#
This guide will show you how to run cardano-node and cardano-cli on your system and some simple examples of how you can interact with the Cardano blockchain.
note
This guide assumes you installed cardano-node and cardano-cli into your system. If not, you can refer to Installing cardano-node guide for instructions on how to do that.
important
This guide does not cover the topic of running a block-producing cardano-node or running a Cardano Stake Pool. For more information regarding that topic, please visit the Stake Pool Operation section.
Configuration Files#
The cardano-node application requires at least four configuration files to run as of writing this article.
- Main Config: It contains general node settings such as logging and versioning. It also points to the Byron Genesis and the Shelly Genesis file.
- Byron Genesis: It contains the initial protocol parameters and instructs the
cardano-nodeon how to bootstrap the Byron Era of the Cardano blockchain. - Shelly Genesis: It contains the initial protocol parameters and instructs the
cardano-nodeon how to bootstrap the Shelly Era of the Cardano blockchain. - Alonzo Genesis: It contains the initial protocol parameters and instructs the
cardano-nodeon how to bootstrap the Shelly Era of the Cardano blockchain. - Topology: It contains the list of network peers (
IP AddressandPortof other nodes running the blockchain network) that your node will connect to.
important
Currently, the cardano-node topology is manually set by the community of network operators in the Cardano blockchain. But an automated p2p (peer-to-peer) system is in the works. For more information visit, Boosting network decentralization with P2P.
For more information about Cardano blockchain eras and upgrades, please visit the Cardano Roadmap.
You can obtain the current Cardano blockchain network configuration files here:
Mainnet / Production#
NetworkMagic: 764824073
https://hydra.iohk.io/build/7370192/download/1/mainnet-config.jsonhttps://hydra.iohk.io/build/7370192/download/1/mainnet-byron-genesis.jsonhttps://hydra.iohk.io/build/7370192/download/1/mainnet-shelley-genesis.jsonhttps://hydra.iohk.io/build/7370192/download/1/mainnet-alonzo-genesis.jsonhttps://hydra.iohk.io/build/7370192/download/1/mainnet-topology.jsonTestnet / Sandbox#
NetworkMagic: 1097911063
https://hydra.iohk.io/job/Cardano/cardano-node/cardano-deployment/latest-finished/download/1/testnet-config.jsonhttps://hydra.iohk.io/job/Cardano/cardano-node/cardano-deployment/latest-finished/download/1/testnet-byron-genesis.jsonhttps://hydra.iohk.io/job/Cardano/cardano-node/cardano-deployment/latest-finished/download/1/testnet-shelley-genesis.jsonhttps://hydra.iohk.io/job/Cardano/cardano-node/cardano-deployment/latest-finished/download/1/testnet-alonzo-genesis.jsonhttps://hydra.iohk.io/job/Cardano/cardano-node/cardano-deployment/latest-finished/download/1/testnet-topology.jsonnote
Each network has a config file, genesis file(s), topology file, and unique identifier called the Network Magic.
This section will be updated when new Cardano networks come online with their respective configuration files and Network Magic.
You might be asking what the difference is between mainnet and testnet and why there are two networks? To put it simply, Cardano is an open-source blockchain, and anyone is free to spin up a network based on Cardano's software components. The mainnet network was the first one established during the start of the Byron era in 2017. And everyone participating in the network agreed that is where all the real value of Cardano lives.
Testing the network's features and capabilities can be expensive and will consume real value. So Input-Output Global has spun up a sandbox or testnet version of the network. Instead of using real ada tokens for transactions, you use the tAda or Test ADA. Alternatively, you can spin up your own custom Cardano network, but that is outside the scope of this guide.
Running the node#
To run cardano-node you enter something like this into the terminal:
cardano-node run \ --topology path/to/mainnet-topology.json \ --database-path path/to/db \ --socket-path path/to/db/node.socket \ --host-addr x.x.x.x \ --port 3001 \ --config path/to/mainnet-config.jsonTo get the complete list of available options, use cardano-node run --help
Usage: cardano-node run [--topology FILEPATH] [--database-path FILEPATH] [--socket-path FILEPATH] [--byron-delegation-certificate FILEPATH] [--byron-signing-key FILEPATH] [--shelley-kes-key FILEPATH] [--shelley-vrf-key FILEPATH] [--shelley-operational-certificate FILEPATH] [--bulk-credentials-file FILEPATH] [--host-addr IPV4] [--host-ipv6-addr IPV6] [--port PORT] [--config NODE-CONFIGURATION] [--validate-db] Run the node.
Available options: --topology FILEPATH The path to a file describing the topology. --database-path FILEPATH Directory where the state is stored. --socket-path FILEPATH Path to a cardano-node socket --byron-delegation-certificate FILEPATH Path to the delegation certificate. --byron-signing-key FILEPATH Path to the Byron signing key. --shelley-kes-key FILEPATH Path to the KES signing key. --shelley-vrf-key FILEPATH Path to the VRF signing key. --shelley-operational-certificate FILEPATH Path to the delegation certificate. --bulk-credentials-file FILEPATH Path to the bulk pool credentials file. --host-addr IPV4 An optional ipv4 address --host-ipv6-addr IPV6 An optional ipv6 address --port PORT The port number --config NODE-CONFIGURATION Configuration file for the cardano-node --validate-db Validate all on-disk database files --shutdown-ipc FD Shut down the process when this inherited FD reaches EOF --shutdown-on-slot-synced SLOT Shut down the process after ChainDB is synced up to the specified slot -h,--help Show this help textcardano-node parameters#
note
In this section, we will use the path /home/user/cardano to store all the cardano-node related files as an example, and please replace it with the directory you have chosen to store the files.
We will focus on six key command-line parameters for running a node:
--topology: This requires the path of the topology.json file that you have downloaded as instructed above.
For example, If you have downloaded the
topology.jsonfile to the path/home/user/cardano/topology.json, then the argument would be something like this:--topology /home/user/cardano/topology.json
--database-path: This expects the path to a directory where we will store the actual blockchain data like blocks, transactions, metadata, and other data type that people stored in the Cardano blockchain. We explore how we can query those kinds of data in the cardano-db-sync section. @TODO: link to the cardano-db-sync section.
For example, if we decide that all files required by
cardano-nodewill be in the path/home/user/cardano/. Then we could create a database directory like this,mkdir -p /home/user/cardano/db. The directory structure would then be something like this:/home/user/cardano/├── db├── testnet-alonzo-genesis.json├── testnet-byron-genesis.json├── testnet-config.json├── testnet-shelley-genesis.json└── testnet-topology.json1 directory, 4 filesAs you may have noticed, we are planning to run a
testnetnode in this example and have downloaded the configuration files into the/home/user/cardano/directory. We also see that we have created thedbdirectory inside/home/user/cardano/successfully. The argument would look something like this:--database-path /home/user/cardano/dbPlease download and move the configuration files to your Cardano directory as shown above to continue following this guide.
--socket-path: This expects the path to the unix socket or named pipe path that the cardano-node will use for IPC (Inter-Process-Communication).
The
cardano-nodeuses IPC (Inter-Process-Communication) for communicating with other Cardano components likecardano-cli,cardano-wallet, andcardano-db-sync. In Linux and MacOS it uses something called unix sockets and Named Pipes in Windows.Here is an example
--socket-pathargument for Linux:--socket-path /home/user/cardano/db/node.socketAs you can see, the argument points to a file since unix sockets are represented as files (like everything else in Linux). In this case, we put the socket file in the
dbdirectory that we have just created before.In Windows, the
--socket-pathargument would look something like this:--socket-path "\\\\.\\pipe\\cardano-node-testnet"As you may notice, it's like a network
URIor a networkPaththan a file. It is a crucial difference that you will have to be aware of depending on your operating system. You can replace the stringcardano-node-testnetin the argument with whatever you like. This example path is used in the Daedalus Testnet Wallet for Windows.
--host-addr: This expects the IP Address of the machine that cardano-node will be running. Other nodes will use this address in their topology.json file to connect to your node if you are planning to run it as a relay node.
Here is an example
--host-addrargument:--host-addr 192.168.0.1In this case, we expect nodes in your LAN (Local Area Network) to connect via
192.168.0.1, assuming that theIP Addressof the machinecardano-nodeis running on; replace it with your realIP Address. If you don't expect or need external nodes to connect to your node, you can use the loopback address127.0.0.1. If you have multiple network interfaces and unsure what to use, you can simply use0.0.0.0to accept connections from any network interface.
--port: In conjunction with the IP Address, we will also set the port that your cardano-node will use for listening to any incoming connection.
Here is an example
--portargument:--port 1337You can choose whatever
portnumber you like, but it is recommended to useportnumbers1024and above. See Registered Port for more information.
--config: This expects the path to the main configuration file that we have downloaded previously.
Here is an example
--configargument:--config /home/user/cardano/testnet-config.jsonPlease make sure that the
alonzo-genesis.json,byron-genesis.jsonandshelley-genesis.jsonare in the same directory as theconfig.json.
Here is a realistic example for running cardano-node:
cardano-node run \--config /home/user/cardano/testnet-config.json \--database-path /home/user/cardano/db/ \--socket-path /home/user/cardano/db/node.socket \--host-addr 127.0.0.1 \--port 1337 \--topology /home/user/cardano/testnet-topology.jsonIf you have everything set correctly, you should see something like this:
Listening on http://127.0.0.1:12798[cardano.node.networkMagic:Notice:5] [2021-05-20 12:17:10.02 UTC] NetworkMagic 1097911063[cardano.node.basicInfo.protocol:Notice:5] [2021-05-20 12:17:10.02 UTC] Byron; Shelley[cardano.node.basicInfo.version:Notice:5] [2021-05-20 12:17:10.02 UTC] 1.27.0[cardano.node.basicInfo.commit:Notice:5] [2021-05-20 12:17:10.02 UTC] 9a7331cce5e8bc0ea9c6bfa1c28773f4c5a7000f[cardano.node.basicInfo.nodeStartTime:Notice:5] [2021-05-20 12:17:10.02 UTC] 2021-05-20 12:17:10.024924 UTC[cardano.node.basicInfo.systemStartTime:Notice:5] [2021-05-20 12:17:10.02 UTC] 2019-07-24 20:20:16 UTC[cardano.node.basicInfo.slotLengthByron:Notice:5] [2021-05-20 12:17:10.02 UTC] 20s[cardano.node.basicInfo.epochLengthByron:Notice:5] [2021-05-20 12:17:10.02 UTC] 21600[cardano.node.basicInfo.slotLengthShelley:Notice:5] [2021-05-20 12:17:10.02 UTC] 1s[cardano.node.basicInfo.epochLengthShelley:Notice:5] [2021-05-20 12:17:10.02 UTC] 432000[cardano.node.basicInfo.slotsPerKESPeriodShelley:Notice:5] [2021-05-20 12:17:10.02 UTC] 129600[cardano.node.basicInfo.slotLengthAllegra:Notice:5] [2021-05-20 12:17:10.02 UTC] 1s[cardano.node.basicInfo.epochLengthAllegra:Notice:5] [2021-05-20 12:17:10.02 UTC] 432000[cardano.node.basicInfo.slotsPerKESPeriodAllegra:Notice:5] [2021-05-20 12:17:10.02 UTC] 129600[cardano.node.basicInfo.slotLengthMary:Notice:5] [2021-05-20 12:17:10.02 UTC] 1s[cardano.node.basicInfo.epochLengthMary:Notice:5] [2021-05-20 12:17:10.02 UTC] 432000[cardano.node.basicInfo.slotsPerKESPeriodMary:Notice:5] [2021-05-20 12:17:10.02 UTC] 129600[cardano.node.addresses:Notice:5] [2021-05-20 12:17:10.05 UTC] [SocketInfo 0.0.0.0:9999,SocketInfo [::]:9999][cardano.node.diffusion-mode:Notice:5] [2021-05-20 12:17:10.05 UTC] InitiatorAndResponderDiffusionMode[cardano.node.dns-producers:Notice:5] [2021-05-20 12:17:10.05 UTC] [DnsSubscriptionTarget {dstDomain = "relays-new.cardano-testnet.iohkdev.io", dstPort = 3001, dstValency = 2}][cardano.node.ip-producers:Notice:5] [2021-05-20 12:17:10.05 UTC] IPSubscriptionTarget {ispIps = [], ispValency = 0}[cardano.node.ChainDB:Info:5] [2021-05-20 12:17:10.06 UTC] Opened imm db with immutable tip at genesis (origin) and chunk 0[cardano.node.ChainDB:Info:5] [2021-05-20 12:17:10.06 UTC] Opened vol db[cardano.node.ChainDB:Info:5] [2021-05-20 12:17:10.06 UTC] Replaying ledger from genesis[cardano.node.ChainDB:Info:5] [2021-05-20 12:17:10.07 UTC] Opened lgr db[cardano.node.ChainDB:Info:5] [2021-05-20 12:17:10.07 UTC] Opened db with immutable tip at genesis (origin) and tip genesis (origin)[cardano.node.ChainDB:Notice:33] [2021-05-20 12:17:10.08 UTC] Chain extended, new tip: 1e64e74bd7ac76d6806480a28017deb0aedd356fb61844ec95c429ae2f30c7c3 at slot 0Syncing the blockchain from zero can take a while. Please be patient. If you want to stop syncing, you can do so by pressing CTRL + C while in the terminal. Rerunning the cardano-node run command with the correct parameters will resume syncing the blockchain.
Querying the Cardano Blockchain#
Now that we have cardano-node running and syncing, we can test it out by querying the blockchain tip data; which is the current point your local node is synced. To do this, we use the cardano-cli command-line application.
But before we can do that, cardano-cli and other Cardano software components need to know where the node socket file is located. We saved it to the path /home/user/cardano/db/node.socket in the previous example. The components read the shell environment variable CARDANO_NODE_SOCKET_PATH to find this.
So we will set that in ~/.bashrc or ~/.zshrc, depending on which shell application that you use. In Windows, you can follow this guide: How to Set Environment Variable in Windows.
Add this line to the bottom of your shell profile (MacOS and Linux):
export CARDANO_NODE_SOCKET_PATH="/home/user/cardano/db/node.socket"Once saved, reload your shell/terminal for changes to take effect.
Finally, we can now test querying the blockchain tip of our cardano-node:
- First, run
cardano-nodein a separate terminal for it to start syncing (if not already). - Open another terminal and run the following command
cardano-cli query tip --testnet-magic 1097911063.You should see something like this:
{ "blockNo": 2598870, "headerHash": "e5be38153db4dc639134969e6449f37e105e0c5228f828f76a885968b4423aaf", "slotNo": 27149964}
note
We include --testnet-magic <NetworkMagic> in the parameter for cardano-cli query tip because we are using a testnet node. If you intend to query mainnet instead, please use the --mainnet parameter and make sure your node is connected to the mainnet network.
What you see here is the local tip data of your node. This case, means that you are synced up to blockNo: 2598870 and slotNo: 27149964.
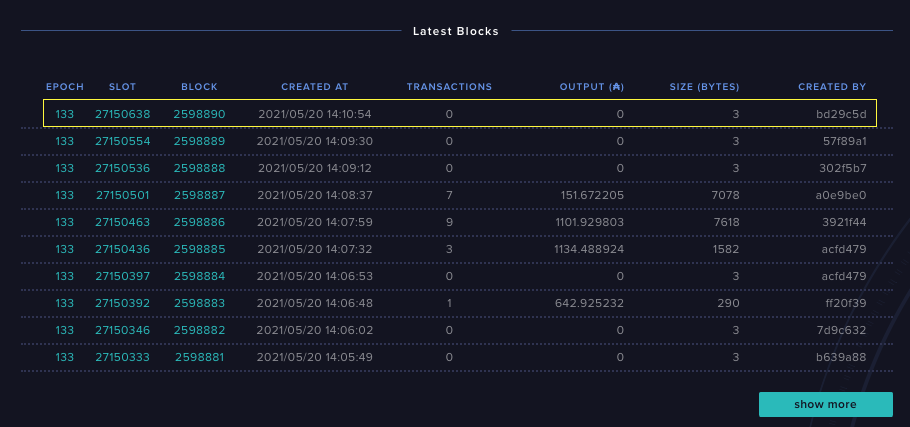
To know whether you are fully synced or not, you can check the Cardano Blockchain Explorer of the relevant network:
Mainnet Explorer#
Testnet Explorer#
https://explorer.cardano-testnet.iohkdev.io
Scroll down to the Latest Blocks section, and you can find the latest network tip.
important
Before making any transactions, make sure you are fully synced to the blockchain network.
Congratulations, you are now ready to explore the world of Cardano! 🎉🎉🎉